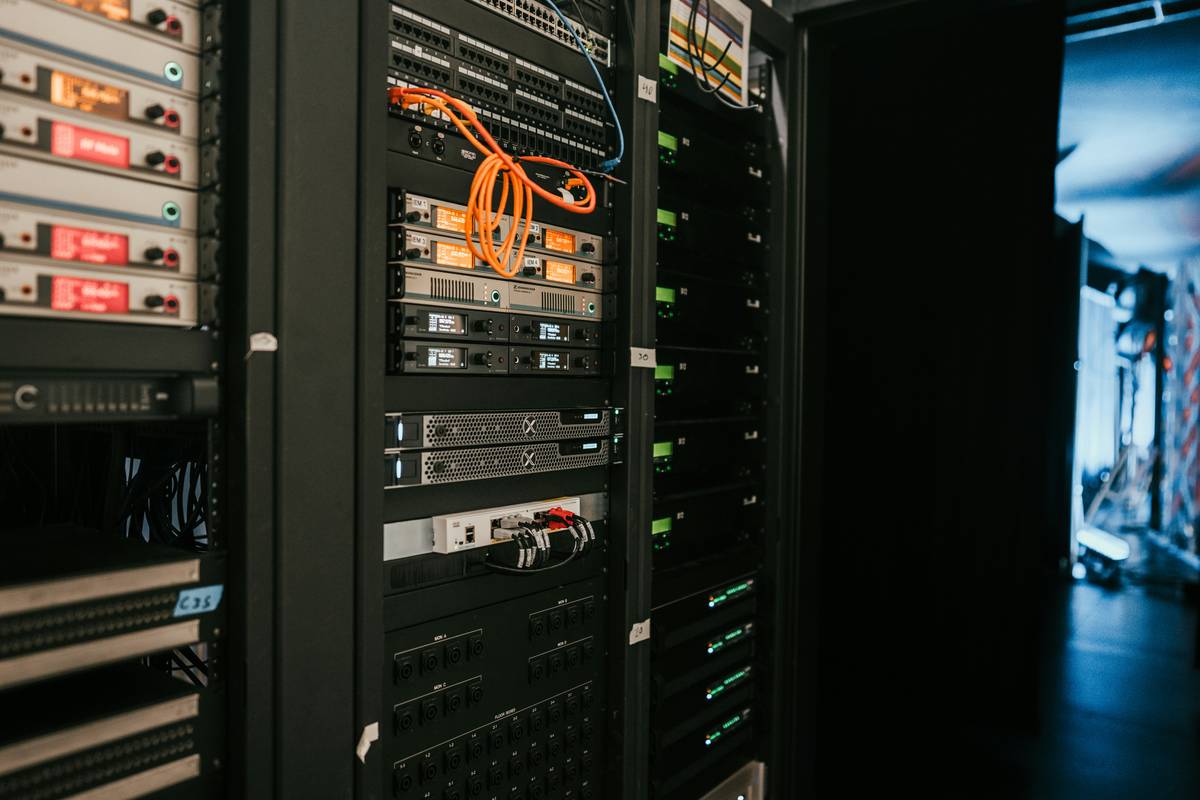
Ever had your website crash during peak traffic, leaving customers frustrated and sales plummeting? Yeah, us too. A system without fault tolerant design is like a house of cards—beautiful until the slightest breeze knocks it down.
In this guide, you’ll discover why fault tolerant design isn’t just for tech giants but essential for anyone managing data systems or websites. You’ll learn:
- What fault tolerant design really means—and why perfectionists hate hearing about its failures.
- A step-by-step process to implement fault tolerance in your infrastructure.
- Pro tips sprinkled with brutal honesty (like, “Backups matter even when they feel boring”).
Table of Contents
- Key Takeaways
- Why Fault Tolerance Matters
- How to Build Fault Tolerant Systems
- Top Tips for Flawless Execution
- Real-World Success Stories
- FAQs About Fault Tolerant Design
Key Takeaways
- Fault tolerant design ensures systems stay operational despite hardware/software failures.
- Redundancy, failover mechanisms, and automated recovery are key components.
- Ideal practices include distributed storage, load balancing, and regular testing.
Why Fault Tolerance Matters
Let’s get real: downtime costs big bucks. According to Gartner, the average cost of IT downtime is around $5,600 per minute. Ouch. But here’s my personal confessional fail—I once ignored adding redundancy to a client’s server setup because “it seemed unnecessary.” Big mistake. One disk failure later, we lost three days’ worth of transactions. Sounds like nails on a chalkboard? Yep.
Fault tolerant design minimizes these risks by ensuring that if one part fails, others seamlessly take over—a true lifesaver in cybersecurity and data management.
How to Build Fault Tolerant Systems
Step 1: Identify Critical Components
Optimist You:* “Start by mapping out every piece of your system.”
Grumpy You: “Yeah, yeah—I promise it’s less painful than debugging everything at once.”*
Step 2: Implement Redundancy
Add backup servers, mirrored databases, and duplicate network paths. Think of it as having spare tires—you hope you don’t need them, but boy, are they clutch.
Step 3: Automate Failover Mechanisms
Set up automatic switches so users never notice disruptions. This keeps things humming along smoothly while you sip coffee—or cry into it after realizing how hard manual fixes can be.
Step 4: Regularly Test Recovery Processes
Rant time! Testing backups isn’t sexy work, but skipping it leads straight to disaster town. Trust me; I’ve been there.
Top Tips for Flawless Execution
- Use load balancers to distribute traffic among multiple servers. Chef’s kiss for reliability.
- Store copies of critical data across geographically separate locations. Because earthquakes shouldn’t wipe out your business.
- Don’t forget software updates—they patch vulnerabilities before hackers exploit them. #NoExcuses
- ⚠️ Terrible Tip Alert: Rely solely on human intervention. Spoiler: Humans sleep sometimes.
Real-World Success Stories
Take NASA’s Mars rovers—they run on insanely robust fault tolerant designs since sending repair crews to space isn’t exactly practical. Closer to home, Amazon Web Services (AWS) uses multi-region deployments to ensure their services rarely go offline, even during massive usage spikes.
FAQs About Fault Tolerant Design
What’s the Difference Between Fault Tolerance vs. High Availability?
High availability aims for minimal downtime, whereas fault tolerance guarantees zero interruption—even during failures.
Is Fault Tolerant Design Expensive?
Short answer: It depends. While initial investment may seem steep, avoiding catastrophic losses makes it worth every penny.
Can Small Businesses Afford Fault Tolerant Systems?
Totally! Cloud platforms offer affordable options tailored for SMBs.
Conclusion
Fault tolerant design might sound intimidating, but it’s simpler than assembling IKEA furniture (okay, maybe not). By implementing redundancy, automating processes, and regularly testing your setups, you can safeguard your systems against unexpected crashes.
“Stay resilient,
Like a Tamagotchi,
Feed your system.”


